You may have heard of the idea that we all respond best to different styles of learning. That is exactly what the seven learning styles theory supports. All of the styles capture an individual strength that likely helps a person retain information more effectively. They each focus on one of the five senses or involve a social aspect. This theory is popular because, by finding an individual learner’s style and tailoring teaching to it, it was thought their efficiency could be improved. The 7 styles of the theory are:
- visual
- kinaesthetic
- aural
- social
- solitary
- verbal
- logical
However, more recent studies have debunked this theory as an effective way of teaching and highlighted it as a neuromyth. This Guardian article says, ‘Such neuromyths create a false impression of individuals’ abilities, leading to expectations and excuses that are detrimental to learning in general, which is a cost in the long term.’
In other words, attempting to put learners into boxes and trying to only give them material that matches their “style” isn’t going to make them retain information any better. Most people benefit from a range of teaching techniques, and utilising different learning methods can actually improve learners’ adaptability.
Nevertheless, it’s certainly true that there are a variety of learning methods people respond to. So, just for fun, we’ve produced 7 different explanations of the 7 styles, each using techniques that learners of that style should find most useful.
Have a look through each one, and ask yourself: do you find them all equally engaging? Is there one (or more) that you prefer above the others? Maybe you have your own learning techniques that aren’t covered by any of the learning styles. Or perhaps you find one style more useful for this exercise, but when learning German verbs or mathematical formulae you know you prefer another? How effectively we learn isn’t just affected by the medium, but the content too.
While the 7 styles theory isn’t going to give you your one definitive style, you might still pick up a few useful techniques.
Visual
Visual or spatial learners supposedly retain information best by viewing pictures or images and respond well to colours and mind maps. These logos represent the main aspect of each learning style. Do you like to learn by remembering symbols and images?
Fill in the form to view a free, full sized, printable version.
Kinaesthetic
According to the theory, kinaesthetic learners are all about doing things physically. Role playing, using things like flashcards or carrying out the action physically can help them learn things better. Print and build this seven-sided die to see whether a hands-on approach could help you retain information.
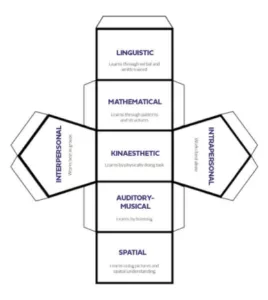
Fill in the form to view a free, full sized, printable version.
Aural
Aural or auditory-musical learners should retain the most information after hearing it. Click below to listen to this recital of the different learning styles: do you tune out or find yourself remembering more than if you read the transcript?
Fill in the form to download and listen to the aural learning style.
Social
Social, or interpersonal learners are meant to work best when they participate in study activities with other people such as quizzing each other or having a study group. Print and use these Top Trumps style cards with a group of friends.

Fill in the form to view a free, full sized, printable version.
Solitary
Solitary, or intrapersonal learners supposedly work best alone. Making notes and reciting them back are useful activities when studying by yourself. Most of us will have to do some solitary revision at some point in our lives, so download and complete this worksheet to see if it works for you.
Fill in the form to view a free, full sized, printable version.
Verbal
Verbal, or linguistic learners are supposed to respond well to written or spoken words, using tools like rhymes and acronyms. Download and complete this worksheet to figure out if these could be techniques that work for you.
Fill in the form to view a free, full sized, printable version.
Logical
Logical, or mathematical learners use logic and structures in order to learn effectively. If you’re good with numbers and statistics, you might find the logical style in this essay helpful. Have a read below:
What are the 7 Different Learning Styles?
Learning styles is the theory that learners can be categorised depending on how they take in information. Therefore, teaching students according to their specific learning styles will result in improved learning. While there is no concrete evidence to support the success of these learning styles, a 2012 study revealed that 93% of teachers in the UK agree that students learn better when they receive information in their preferred learning style.
These learning styles derived from Howard Gardner’s 1960s theory of Multiple Intelligences. This theory states that: “we are all able to know the world through language, logical-mathematical analysis, spatial representation, musical thinking, the use of the body to solve problems or to make things, an understanding of other individuals, and an understanding of ourselves.” This essay plans to outline the seven different learning styles while categorising them into three main categories: personal, sensory and informational. It will then recommend study methods for each type of learner.
1. Personal Learning Styles
The personal category links learning styles which depend on other persons to be present or absent. These are different from other learning styles which focus on how the learner takes in information, instead they depend greatly on the learners’ surroundings and whether they are studying with or without people. These types of styles split into Interpersonal learners or intrapersonal learners.
1.1 Interpersonal Learners
Interpersonal learners work best in groups and social elements help improve their concentration. Debates, group study and interactions are the best methods. Interestingly, while they work best in groups, they also have the most empathy when it comes to others. “Interpersonal intelligence builds on a core capacity to notice distinctions among others – in particular, contrasts in their moods, temperaments, motivations and intentions.”
1.2 Intrapersonal Learners
Intrapersonal learners are also known as solitary learners. Unlike interpersonal learners they work best when studying alone. They are known to be interested in philosophy, psychology and theology because of their proficiency in self-reflection.
“They’re in tune with their inner feelings; they have wisdom, intuition and motivation, as well as a strong will, confidence and opinions,” said a 2008 study on bridging educational divides. Unsurprisingly, these are the most independent learners from all the seven styles. Recommended study methods for intrapersonal learners include keeping a journal and finding a personal interest in the topics being studied.
2. Sensory Learning Styles
The sensory category links learning styles which use the senses. These are split into spatial/visual learners, auditory-musical learners and kinaesthetic learners. According to various studies of the sensory learning styles, roughly 65 percent of the population are visual learners, 30 percent are auditory learners and 5 percent are kinaesthetic learners. However, many students show traits of multiple learning styles.
2.1 Spatial Learners
Spatial learners are visualisers, which is why they’re also known as ‘visual learners’. As educational writer Stacy Mantle describes, these types of learners are good at working with colours and pictures and using the “mind’s eye.” Visual learners use spatial understanding; thus Gardner discusses that their problem solving is useful for navigation and map reading. This type of learning is also helpful for visualising an object from different angles and in playing chess.
2.2 Auditory-Musical Learners
Auditory-musical learners take in information through their sensitivity to rhythm and sound. They have the capacity to discern pitch, rhythm, timbre, and tone. “Good or bad, their response to any music they hear is immediate, and they tend to be more in tune with nature sounds, and the sounds of their environment than their counterparts,” said Gilam in a study about multiple kinds of intelligence. The best methods for auditory-musical learners are to study with music in the background or to turn their notes into rhymes.
2.3 Kinaesthetic Learners
Kinaesthetic learners take in information through the use of their body and touch. Obvious kinaesthetic learners include dancers or surgeons. For these physical learners, a hands-on education and carrying out the activity themselves is more effective than listening to an explanation. According to Mantle, many of these kinaesthetic learners are often misdiagnosed as having Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder, usually because they often have more energy than other types of learners.
3. Informational Learning Styles
The last category for the learning styles is informational, which refers simply to how the brain parses information, many in form of language or data. These learning styles do not depend on the senses or the learner’s social surroundings. Informational learners can be split into linguistic learners or mathematical learners.
3.1 Linguistic Learners
Linguistic learners, which are also known as verbal learners, work best with words. Whether information is spoken or written, these learners memorise information through language use. Gardner states “the linguistic intelligence is activated when individuals encounter the sounds of a language or when they wish to communicate something verbally to another person.” However, this learning style doesn’t correlate exclusively with the spoken word. For example, deaf people could demonstrate linguistic intelligence through the use of signs, according to Gardner.
For linguistic learners, recommended approaches include reading classes and telling stories. So taking notes while reading is a successful method of study.
3.2 Mathematical Learners
As the name implies, mathematical learners work best using numbers, structures and reasoning, this is why they are also referred to as logical learners. According to Mantle, these learners make the best engineers and work by categorising and classifying abstract patterns or relationships. Gardner notes a similarity between mathematical and musical learners, because both are drawn to structural patterns, which can often exist in music.
Conclusion
To summarise, despite the lack of substantial evidence supporting the success of these learning styles, they remain widely popular and are still used in schools throughout the country. According to this Wired article “Parents, understandably, like to think that their children are receiving a tailored education. Teachers, also understandably, like to think that they are sensitive to each child’s needs and many are clearly motivated to find out more about how to fulfil this ideal.” However, while there is still value in tailoring teaching methods based on the content and intended audience, attempting to strictly organise individuals into specific styles is not likely to be helpful, and could even prevent them from developing more rounded learning skills.
Jarrett goes on to describe how “learning is improved (for most everyone) by combining different activities – such as drawing alongside more passive study.” While it is not as useful as once thought for categorising learners, the 7 learning styles theory may still be of some use in making both teachers and learners alike aware of a greater variety of learning techniques and methods.
Our courses are designed to embed these fundamental learning styles so that our learners can cover the curriculum in a way that suits them. You can find our CIPD courses here, where you can request a brochure or start online today.
CIPD Level 3 HR Courses: The CIPD Level 3 Certificate in People Practice is ideal for anyone looking to start a career in either HR or Learning and Development.
CIPD Level 5 HR Courses: The CIPD Level 5 Associate Diploma in People Management will help you build on your existing HR knowledge.
CIPD Level 5 L&D Courses: The CIPD Level 5 Diploma in Organisational Learning and Development is the most comprehensive course available for L&D professionals, ideal for you if you want to formalise your existing experience, skills and knowledge.
CIPD Level 7 HR Courses: The CIPD Level 7 Advanced Diploma is aimed at expanding learners’ autonomy so they can strategically direct organisations and their people.
If you aspire to become a digital marketing manager or explore the senior level of your career have a look at the squared digital marketing programme.
Did you find any of these techniques helpful? You probably don’t fit neatly into one “style” in the way people used to think, but we hope this has helped you to figure out some of your preferred learning methods so you can plan for future study sessions!

 11 min read
11 min read 





